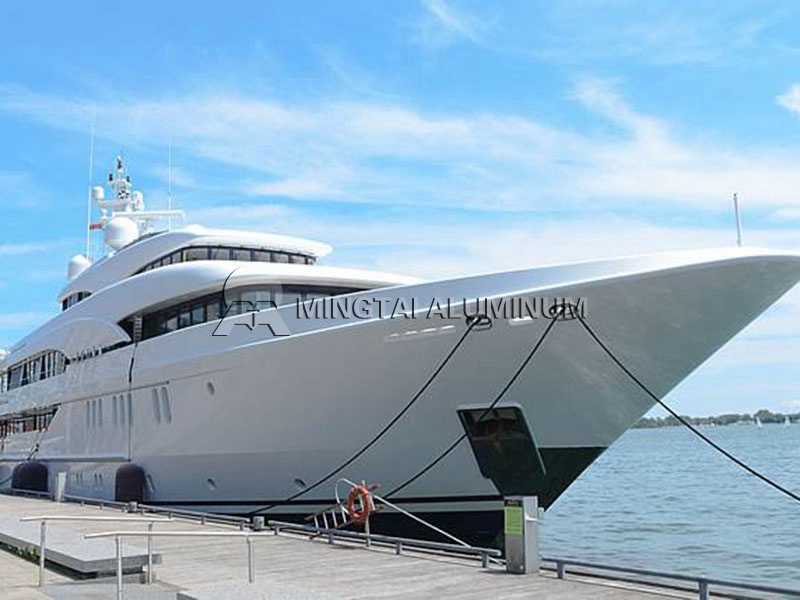
Marine Grade Aluminum: Ship Aluminum Alloy
Sample: A4 Sized
Payment Terms: L/C,D/P,T/T
Delivery time: Within 15-30 Days
Email Us:sale06@mingtai-al.com
Aluminum alloy can be divided into two major categories of deformation and casting. The former is used for plastic deformation processing of various semi-finished products – plates, strips, foils, tubes, rods, profiles, wires, forgings, and the latter is used for casting various die castings.
Casting products, deformed aluminum alloys are more widely used in shipbuilding. Because aluminum alloy has high specific strength, strong resistance to seawater corrosion, weldability, easy forming, no low temperature brittleness, no magnetism, etc., its application in shipbuilding can effectively reduce ship quality, improve stability, increase speed, etc. . Therefore, aluminum alloy has become one of the current Marine Grade Aluminum: one of the main structural materials for shipbuilding.
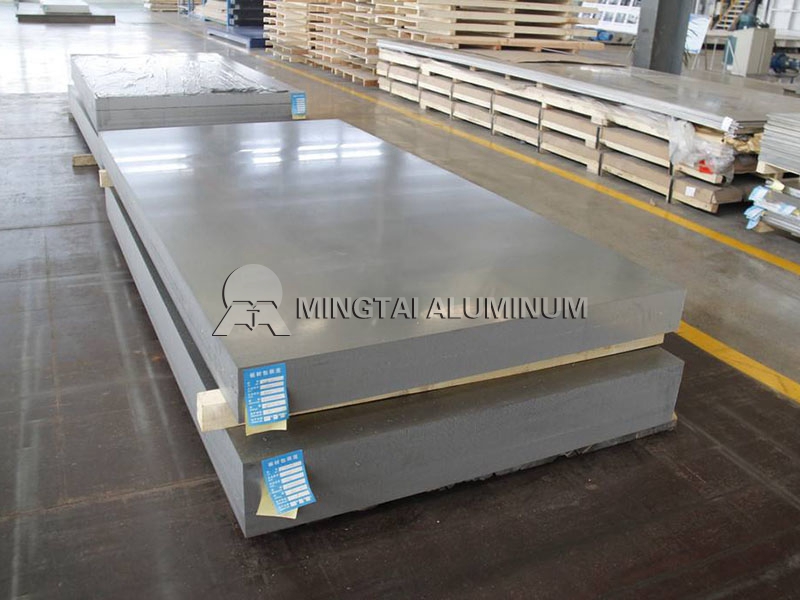

The application of deformed aluminum alloys in shipbuilding in various countries, from the superstructure of large surface ships, the construction of thousands of tons of all-aluminum marine research vessels, ocean-going merchant ships and passenger ships, to hydrofoil, hovercraft, passenger ferries, catamaran passenger ships, Some high-speed passenger ships and military speedboats such as transportation boats and landing crafts use some deformed aluminum alloys.
Cast aluminum alloy is mainly used for pump, piston, armor and fish, mine shell and other parts. The mine (torpedo) shell is preferably made of super-strength hard aluminum 7xxx alloy extruded seamless thick-walled tube. The launch tube can also be made of an aluminum alloy tube.

Marine Grade Aluminum: Marine alloy chemical composition
Since its application in ships, ships, ships and boats in 1891, aluminum alloy materials have been used more and more widely after more than 120 years of development, and have become one of the most promising materials for the shipbuilding industry. It was first applied to aluminum-copper alloys in which the aluminum alloy on the ship was Ni, and then Al-Cu-Mg alloys were used, but their main disadvantage was poor corrosion resistance, which limited their application.
In the 1930s, the 6061-Tb alloy was used and the hull was manufactured by riveting;
In the 1940s, a 5xxx alloy that can be welded and corrosion resistant was developed.
In the 1950s, tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding technology was adopted. During this period, the application of aluminum alloy in shipbuilding was very fast. In the 1960s, the US Navy developed 5086-H32 and 5456-H321 alloys belonging to Al-Mg alloy. Plate, 5086-H111 and 5456-H111 alloy extruded profiles, due to the use of H116 and H117 state, eliminate the precipitation of the network along the crystal, solving their problem of spalling corrosion and intergranular corrosion, which is developed in the ship aluminum alloy Significant progress in the area. Subsequently, due to the need for materials with higher yield strength, the 6xxx series alloy with good seawater corrosion resistance is widely used in shipbuilding. For a long period of time, the hull aluminum alloy is mainly in the 5xxx series alloy and the 6xxx series alloy. The choice, while the Soviet Union used 2xxx alloys as the material of the speedboat shell. In recent years, the research on the medium-strength weldable 7xxx series alloy has been temporarily increased, and some progress has been made, which has been applied and developed in shipbuilding.
After the 1970s, the rationalization and light weight of ship structures were paid more and more attention. The superstructures and armor of large ships began to use aluminum alloys in large quantities. To this end, a number of superstructures and armored aluminum alloys were developed during this period, including extruded profiles of special specifications, large-scale extruded panels and castings.

In Japan, mainly 5083, 5086 and 6N01 alloys are used, and almost all of the structures used are 5083 aluminum plates, but the magnesium content should be controlled below 4.9% to prevent stress corrosion cracking (SCC), but the United States also uses 5456 alloy. The magnesium content is higher than that of the 5083 alloy, but heat treatment measures to prevent stress corrosion should be taken.
Ship aluminum alloy can be divided into hull structure alloy, armored alloy and welded filler alloy. The chemical composition of JIS (Japanese Industrial Standard) aluminum alloy for shipbuilding in Japan is shown in the table. At present, the aluminum alloys used in the hull structure are mainly 5083, 5086 and 5456.